| Potentialities - 1
|
| |
|
| |
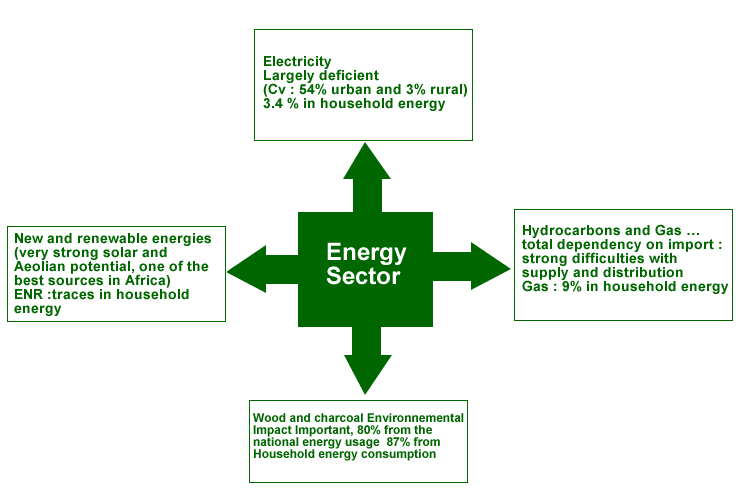
Diverse sources of energy
and a difficulty supply context |
| |
|
| |
 |
| |
|
| Potentialities - 2 |
| |
|
| |
National energy resources
|
| |
| Energy
Sources |
Current Potential
|
Comments |
| Wood |
317 000 (ha) |
|
| Wind |
~ 7 m/s(10 m above the ground)7.641
KWh/m2/year |
Important in force and regularity
- Aeolian Parks |
| Solar |
Duration 8h/dIncidental energy 4,6
KWh/m2/d |
Important potentialSeasonal regularityHomogeneous
spatial Repartition |
| Hydrocarbons and Gas |
Gas 70 billion m3 500 million barrels
of oil |
Reserves - possibility of a gas turbine
plant |
| Hydro-electric |
Weak 30 MW |
Manantali Dam (15% of 200MW) |
| Peats |
650 tons |
Exploitable Reserve (River Delta) |
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
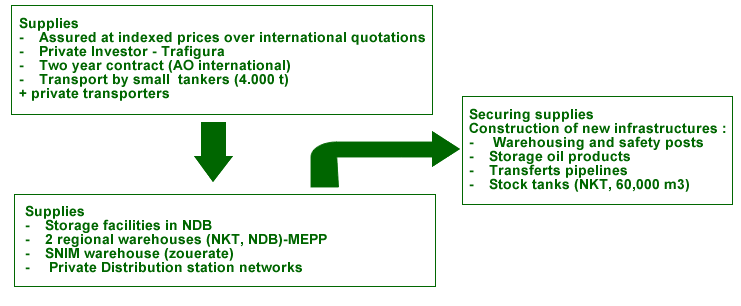
National
market Demand
Oil products Import … 439.000 TM (heavy fuel,
diesel fuel and GPL)
|
| |
 |
| |
|
| |
National Demand market
Butane Gas Import …22.000 TM/an (6.30 Millions
US$)
|
| |
|
Distribution
- Nouakchott : 75%
- Nouadhibou : 15%
- Very slow Evolution in rural area
- Distributors :
- SOMAGAZ (SEM) Gvt (34%) , Naftal
(33%) Private Mauritanian companies
(33%)
- q Some private investors (timid
interventions)
- q SOMAGAZ : Storage Centers of
(4)/barreling trucks / 250,000 bottles
- q Imports : Northern area(Naftal,
Algeria) / Southern area (international
market by AO)
|
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
Constraints
- High prices vs Charcoal
- Very variable freight rates due
to : limited duration contracts, commitment
level and limited number of traders
- Decrepit packaging
- Lack of safety norms in transport
and storage
- Shortage of maintenance and investment
means
|
|
|
| |
|
| |
Renewable
Energies
Substitution and promotion
solution for clean energies
|
| |
|
| |
|
Solar
Solar energy cannot be exploited for
one single application: Lighting and
accessories for refrigeration, audio
and audiovisual equipment, water pumps
in small rural communities
No thermo solar plant / Go beyond
the scope of small solar Kits
Mauritania barely benefit from the
solar energy abundance
Applications: Solar water heaters/
Solar Micro-ovens/Solar dryers (dehydratation
and conservation of food products)
Wind
- Unexploited potential /no large
Aeolian parks (also respond to urban
demand: energy destined to be injected
in the network)
- Lack of experience and experience
sharing / Weak investments
- Production Cost of high KWh (8 US
cents, BAD-2004)
- Lack of skilled technical labor
- Multiple scale projects : Large
scale (urban) and small scale (rural)
Example of Morocco (190 GWh are produced
by the Koudia El Beidia Aeolian park)
|
|
|
| |
|
| |
Access
to funding aimed at promoting private investment
in Africa (ex. UE / GEEREF…)
The national Electricity market
is largely deficient
Current available supply: 76MW
(thermal plants)
Poorly satisfying demand: 54% urban and 3% rural
Important and accessible sub-regional market:
major deficit in Mauritania as well as in neighboring
countries (Mali and Senegal)
|
| |
 |
| |
Developing Thermal Plant (fuel)
|
| |
|
| |
Major
reforms - 1
Strategic Reforms
- Liberalization activities related to the
importation, storage and distribution of oil
products
- efinition of a transparent price policy oil
products (establishment of regulation body,
National Commission of Hydrocarbons, CNH)
- Suppression of national territory monopoly
for electricity services delivery
- Creation of a regulation framework promoting
the private sector participation in electricity
services delivery
- Preparation of privatization conditions for
SOMELEC (to serve 20 urban plants and 83% the
urban population)
Major reforms - 2
Two strategic partners for private
investors
- Creation of a Rural Electrification Development
Agency (ADER) - 2000 - A private corporation
- promote the development of public and private
investments in rural electrification
- Creation (2001) of a Agency for Universal
Access to Basic Services (APAUS) - rural and
semi-urban areas - Electrification program in
17 semi-urban communities
Anticipated short and medium term
Reforms 1
- Improvement of the regulation framework promoting
energy production from Aeolian and solar source
- Reduction of the high cost of producing wind
and solar energy
- Strengthening the technical capacities of
producing wind and solar energy
- Promoting the involvement of the private
sector in renewable energies
- Implementing pilot medium and large scale
renewable energy projects
Anticipated short and medium term
Reforms 2
- Exploring the possibility of implementing
gas turbines to produce electricity (natural
gas potential)
- Privatization of the national Electricity
Company
- Increase the production of electricity in
Manantali
|
| |
|